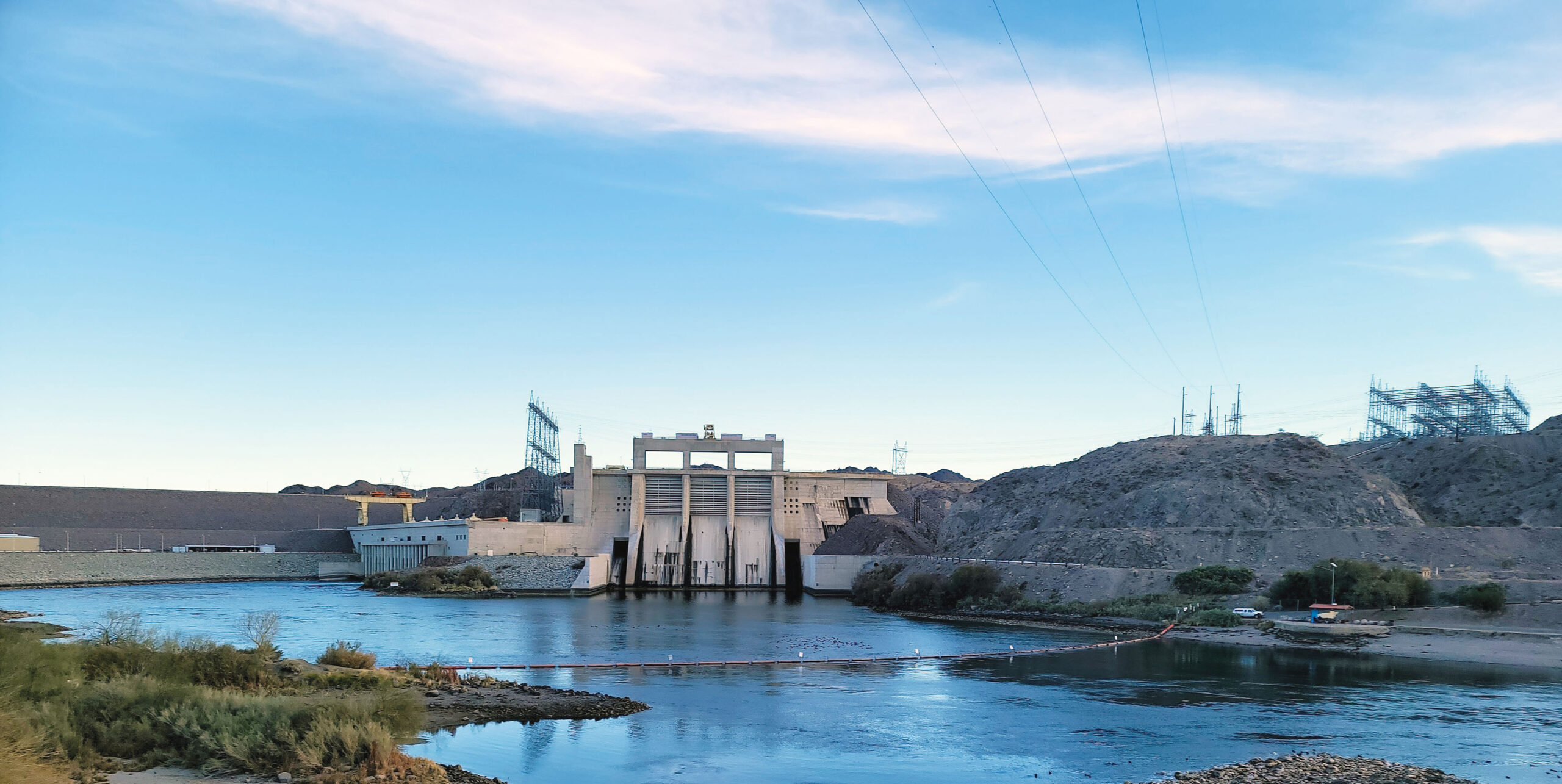
In a landmark agreement that promises to usher in a new era of water management in the Southwest, seven states have reached a consensus to cut water use from the Colorado River over the next three years. This decision, aimed at preventing reservoirs from falling to critically low levels, has significant implications for Mohave County and the state of Arizona.
The Impact of a 23-Year Drought on Colorado River Levels
This agreement comes at a time when the Colorado River, a lifeline for states from the Rocky Mountains to the U.S.-Mexico border, has been grappling with record-low levels following 23 years of drought exacerbated by rising temperatures due to climate change.
New Deal: A Shift in Water Management Strategy for Southwest States
The deal represents a significant shift in water management strategy and a testament to the power of cooperation in the face of shared adversity.
Commitments and Contributions: States Agree on Water Reduction Plan
The agreement, announced on May 22, 2023, commits California, Arizona, and Nevada to reduce water use by 3 million acre-feet between now and the end of 2026. This reduction is equivalent to about 14% of the total water consumption across the Southwest.
The majority of the cuts will come from California, with Arizona and Nevada also contributing significant reductions. These reductions are a testament to the commitment of all states involved, including Arizona, to address the water crisis.
Federal Government’s Role in Addressing Falling Reservoir Levels
The deal also includes a provision for the federal government to step in and make additional cuts should the levels of Lakes Mead and Powell drop further. These cuts would be triggered if Mead fell to 1,000 feet and Powell fell to 3,500 feet – just over each reservoir’s dead-pool level.
Ensuring Continuity in River Flow Amid Overuse
The Colorado River system has been on the precipice of crisis after decades of overuse. Officials grew concerned as dams at Lake Mead and Lake Powell neared “dead pool” status — when flow would be cut off to lower regions of the river as water levels dropped too low to pass through the dams.
Fostered Cooperation: The Biden Administration’s Role
The agreement comes in the wake of the Biden administration’s commitment to working with states, tribes, and communities in the West to find consensus solutions in the face of climate change and sustained drought.
Engaging in Discussion: Key Water Officials and the Role of Negotiation
The deal-making took place over a series of official and unofficial meetings in various locations throughout the West. These meetings brought together key water officials, including Tom Buschatzke, the director of the Arizona Department of Water Resources, and his counterparts from California and Nevada.
Anticipated Impact of the Agreement on Reservoir Levels
The agreement is expected to have a significant impact on water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell. The cuts are projected to prevent Lake Mead, the nation’s largest reservoir, from reaching “dead pool” over the next three years.
Collaboration: A New Approach to Water Management
The deal also marks considerable cooperation among the lower-basin states, tribes, water agencies, and agricultural irrigation districts that have long relied on the Colorado River as a lifeline.
Potential Benefits for Mohave County and Arizona
For Mohave County and other areas in Arizona, the agreement could bring potential benefits. The federal money from the Inflation Reduction Act will fund water conservation programs to compensate farmers, tribal communities, cities, and other water users that take steps to voluntarily and temporarily cut back on water use.
Challenges Ahead: The Temporary Nature of the Agreement
Despite the optimism surrounding the agreement, there are still challenges ahead. The deal is only a temporary solution, with the proposed changes set to expire in 2026.
Future Perspectives and the Importance of Cooperation
The historic agreement marks a new era for water management in the Southwest. It represents a significant step towards addressing the long-term challenges facing the Colorado River system. For Mohave County and the state of Arizona, it offers a path forward in the face of ongoing drought and climate change.
The Role of Local Residents in Water Conservation
As we move forward, it is crucial for local residents to support water conservation efforts and the implementation of the agreement. The future of our water supply depends on our collective action and commitment to sustainable water management.
Emphasizing the Broader Implications of the Agreement
This agreement is not just about water; it’s about the future of our communities, our economy, and our way of life. It’s about the resilience of Mohave County and the entire state of Arizona as we navigate the challenges of climate change and water scarcity. It’s a story of cooperation, innovation, and the indomitable spirit of the Southwest.